
You can try using the Law of Sines or the Law of Cosines to determine side lengths in other triangles. While the formula shows the letters b and h, it is actually the pattern of the formula that is. But - what if it's not a right triangle? If you change that angle in the triangle there can obviously be any number of possibilities for the hypotenuse! Thus, you need more information to solve the problem. The general formula for the area of a triangle is well known. Plug those into the appropriate places in the Pythagorean equation:Īs you can see, it is pretty simple to use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the missing side length of a right triangle. Pythagoras theorem states that in a right triangle (or right-angled triangle) the sum of the squares of the. Suppose you know that one leg is 5 and the hypotenuse (longest side) is 13. Geometry Formulas Triangles - Pythagoras Theorem. If you are given the hypotenuse and one of the legs, it's going to be slightly more complicated, but only because you have to do some algebra first. Since we are given that the two legs of the triangle are 3 and 4, plug those into the Pythagorean equation and solve for the hypotenuse: To calculate the area of a triangle in Excel, you can use the standard formula, adapted with Excels math operators. Just square the sides, add them, and then take the square root. Next, find the area of the two triangular faces, using the formula for the area of a triangle: 1/2 base x height. Find the areas of each of the three rectangular faces, using the formula for the area of a rectangle: length x width. If you're given the lengths of the two sides it is easy to find the hypotenuse. Area × b × h The formula works for all triangles. Here are the steps to compute the surface area of a triangular prism: 1. The hypotenuse is the longest side of a right triangle. The theorem states that the hypotenuse of a right triangle can be easily calculated from the lengths of the sides. One of the more famous mathematical formulas is \(a^2+b^2=c^2\), which is known as the Pythagorean Theorem. The segment AO is the radius of the circumcircle of triangle ΔABC.If I'm given a right triangle and two of its sides, how can I find the length of the third side? Can I do this if it's not a right triangle? Answerįinding the missing side of a right triangle is a pretty simple matter if two sides are known. It is easy to see why the length of B'C' = a/2 (it is a side of the medial triangle). Thus, the quadrilateral AB'OC' is a cyclic quadrilateral. Triangles AB'O and AC'O are both right triangles. We can use this triangle to find the area of the triangle in terms of the sides of the triangle. Acute Angled Triangle: A triangle having all its angles less than 90. Sometimes it is specified as having two and only two sides of equal length, and sometimes as having at least two sides of equal length, the latter version thus including the equilateral triangle as a special case.
Rectangles have four sides and four right (90) angles. Now consider: In other words, the coefficient of proportionality is 2. Equilateral Triangle: All the sides are equal and all the three angles equal to 60. According to Wikipedia: ' In geometry, an isosceles triangle is a triangle that has two sides of equal length. The Pythagorean Theorem In any right triangle, a2 + b2 c2 where c is the length of the hypotenuse and a and b are the lengths of the legs. Step 2 as by condition, so: Consider: The coefficient of proportionality is 2. Also, the angles opposite these equal sides are equal. Isosceles Triangle: It has two equal sides. The length of the bisectors from O to the sides of the triangle, OA', OB', and OC', are given as x, y, and z, respectively. Scalene Triangle: All the sides and angles are unequal. We have a triangle whose perpendicular bisectors meet at the common point O. However, it turns out to be the same as Heron's formula when Heron's formula is simplified. At first, I thought it was a new formula. I discovered a method for deriving formula for the area of a triangle based on the sides of a triangle using the perpendicular bisectors. This means that there exists a formula for the triangle in term of the sides, giving a unique area. Substituting angles A and B into our previous equation, A + B + BCA 180, where BCA C. Similarity Geometry (whole content) Mathematics Khan Academy Congruence and Similarity Lesson (article) Khan Academy Similar Triangles- Formula.
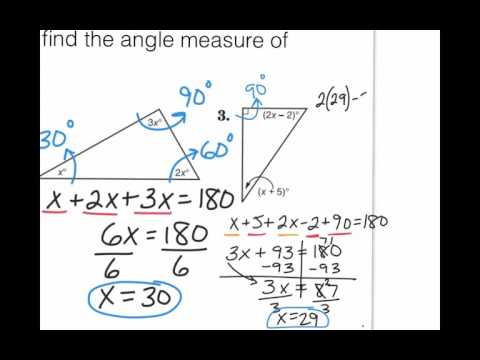


Given any 3 lengths, there can only be 1 triangle that can be formed. We will include this in the first step of the problem solving strategy for geometry applications. In addition, since these applications will all involve shapes of some sort, most people find it helpful to draw a figure and label it with the given information. One of the most famous formulas for triangles is the formula for the area of a triangle based on the sides of the triangle. The geometry formula will name the variables and give us the equation to solve.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
